System Design of DTaaS Authorization Microservice
DTaaS requires backend authorization to protect its backend services and user workspaces. This document details the system design of the DTaaS Auth Microservice which is responsible for the same.
Requirements
For our purpose, we require the Auth MS to be able to handle only requests of the general form ”Is User X allowed to access /BackendMS/example?”.
If the user’s identity is correctly verified though the GitLab OAuth2 provider AND this user is allowed to access the requested microservice/action, then the Auth MS should respond with a 200 (OK) code and let the request pass through the gateway to the required microservice/server.
If the user’s identity verification through GitLab OAuth2 fails OR this user is not permitted to access the request resource, then the Auth MS should respond with a 40X (NOT OK) code, and restrict the request from going forward.
Forward Auth Middleware in Traefik
Traefik allows middlewares to be set for the routes configured into it. These middlewares intercept the route path requests, and perform analysis/modifications before sending the requests ahead to the services. Traefik has a ForwardAuth middleware that delegates authentication to an external service. If the external authentication server responds to the middleware with a 2XX response codes, the middleware acts as a proxy, letting the request pass through to the desired service. However, if the external server responds with any other response code, the request is dropped, and the response code returned by the external auth server is returned to the user
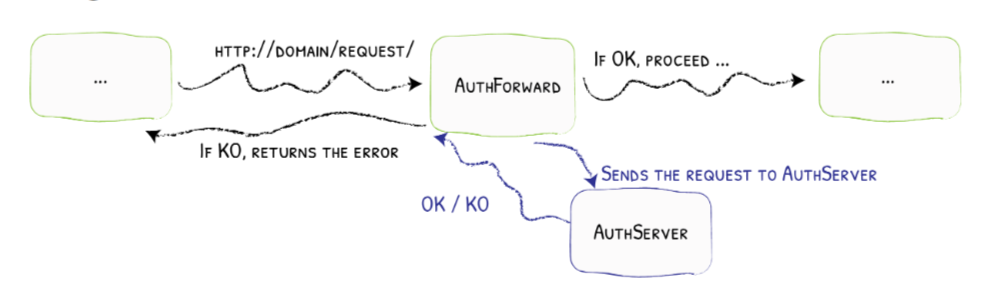 (source:
Treafik documentation)
(source:
Treafik documentation)
Thus, an Auth Microservice can be integrated into the existing gateway and DTaaS system structure easily by adding it as the external authentication server for ForwardAuth middlewares. These middlewares can be added on whichever routes/requests require authentication. For our specific purpose, this will be added to all routes since we impose atleast identity verification of users for any request through the gateway
Auth MS Design
The integrated Auth MS should thus work as described in the sequence diagram.
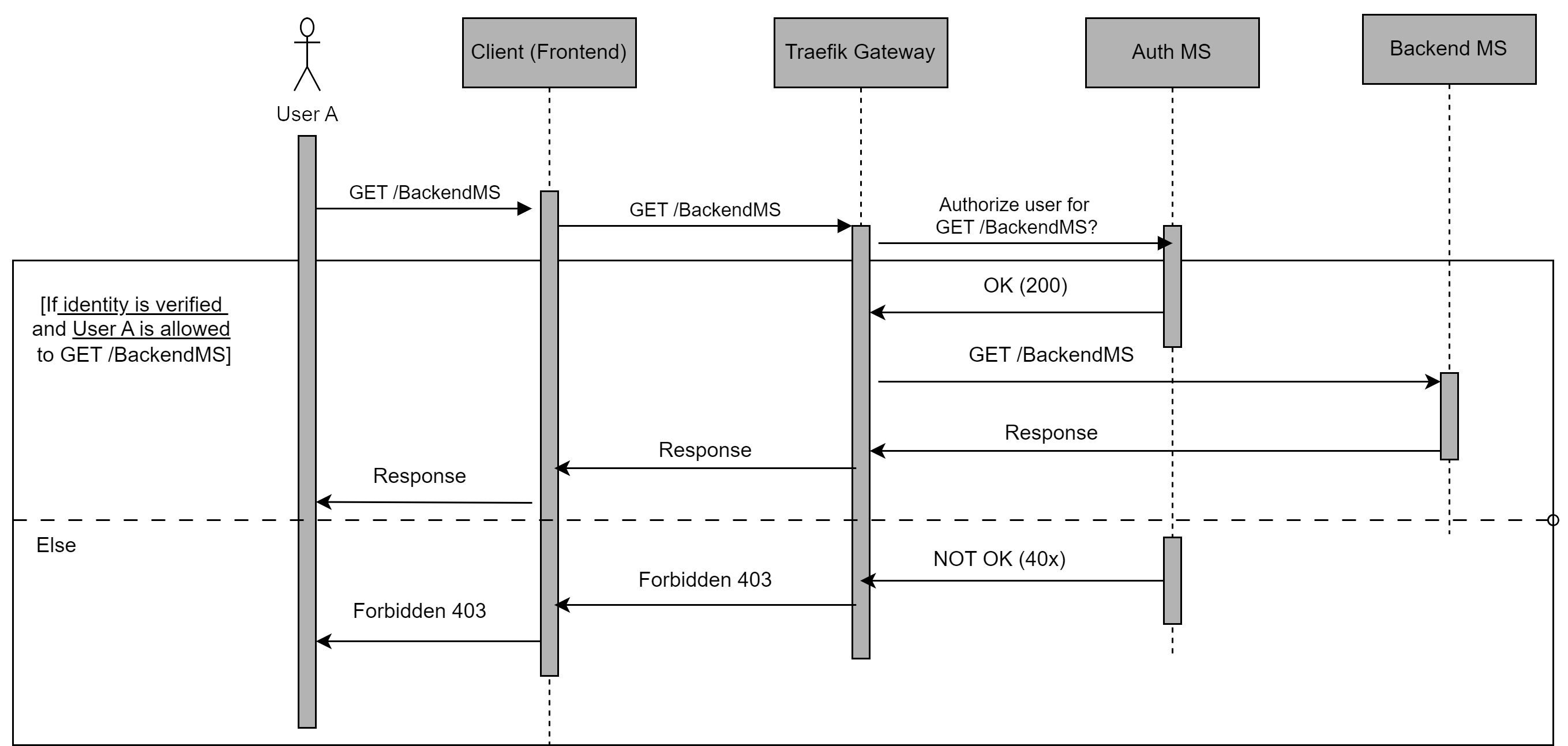
-
Any request made by the user is made on the React website, i.e. the frontend of the DTaaS software.
-
This request then goes through the Traefik gateway. Here it should be interrupted by the respective ForwardAuth middleware.
-
The middleware asks the Auth MS if this request for the given user should be allowed.
-
The Auth MS, i.e. the Auth server verifies the identity of the user using OAuth2 with GitLab, and checks if this user should be allowed to make this request.
-
If the user is verified and allowed to make the request, the Auth server responds with a 200 OK to Traefik Gateway (more specifically to the middleware in Traefik)
-
Traefik then forwards this request to the respective service. A response by the service, if any, will be passed through the chain back to the user.
-
However, If the user is not verified or not allowed to make this request, the Auth server responds with a 40x to Traefik gateway.
-
Traefik will then drop the request and respond to the Client informing that the request was forbidden. It will also pass the Auth servers response code