Working with GitLab
The DTaaS platform relies on GitLab for two purposes:
- OAuth 2.0 authorization service
- DevOps service
The admin documentation covers the OAuth 2.0 authorization configuration. This guide addresses the use of git commands and project structure for the GitLab DevOps service within the DTaaS.
Preparation
The first step is to create a GitLab project with the username in the GitLab user group named dtaas.
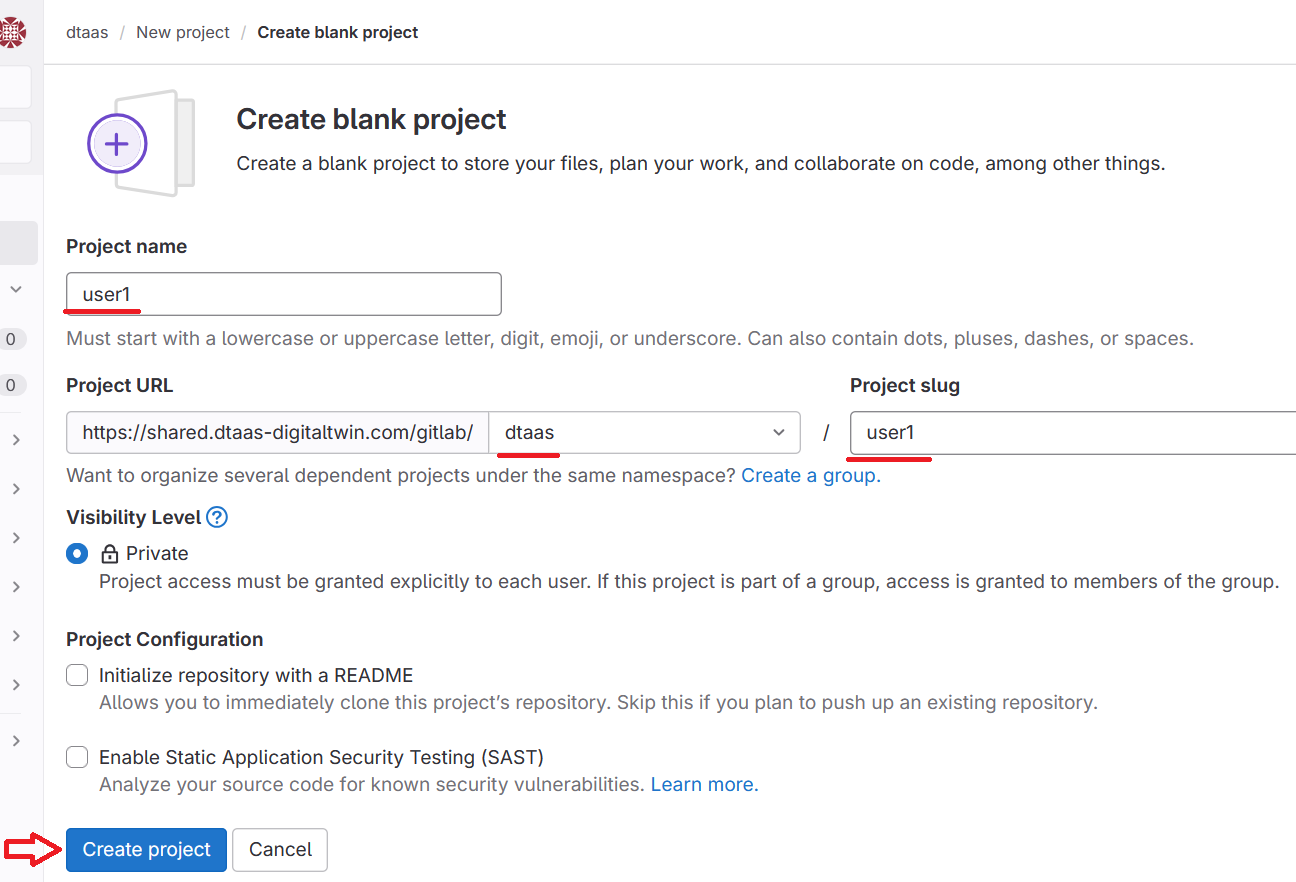
The user must have ownership permissions over the project.
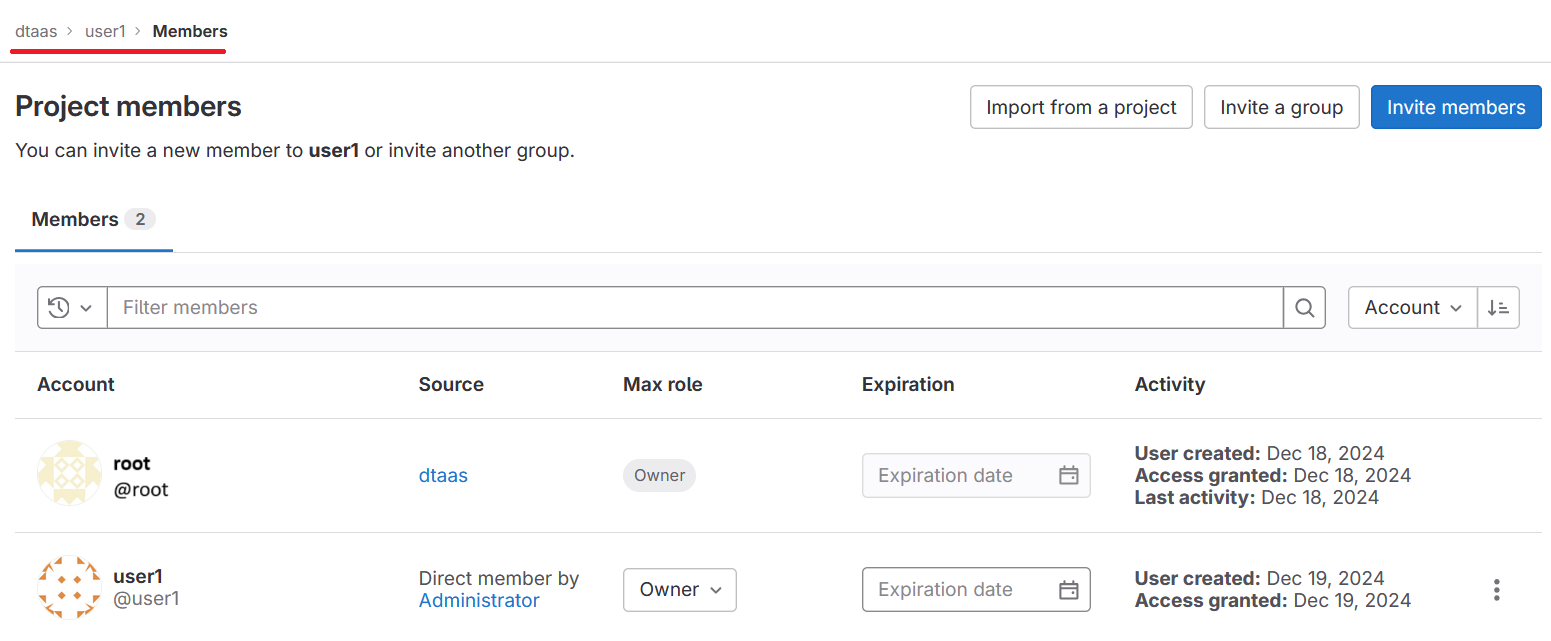
Warning
The DTaaS website expects a default branch named
main to exist. The website client performs all git
operations on this branch.
The preferred default branch name can be changed in the
settings page.
Git commands
Standard git commands and workflows should be utilized. There are two methods for using a GitLab project as a remote git server:
- Over SSH using a personal SSH key
- Over HTTPS using personal access tokens (PAT)
This tutorial demonstrates the use of PAT for working with the GitLab server.
The first step is to create a PAT.
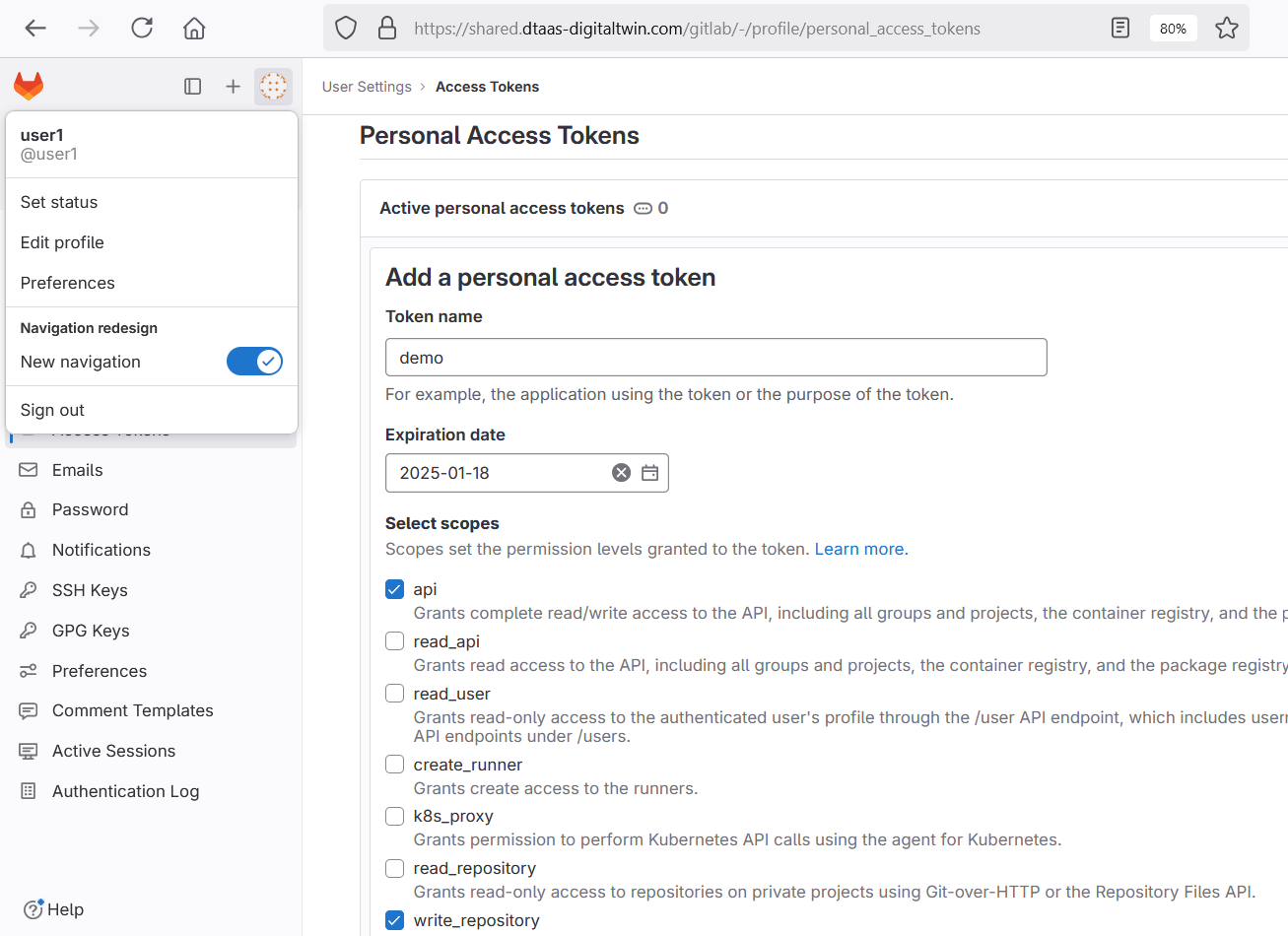
This token should be copied and used to clone the git repository.
Library Assets
GitLab is used to store the reusable Library assets of all users. A mandatory structure exists for storing and using Library assets including digital twins. A properly initialized GitLab project should have the following structure.
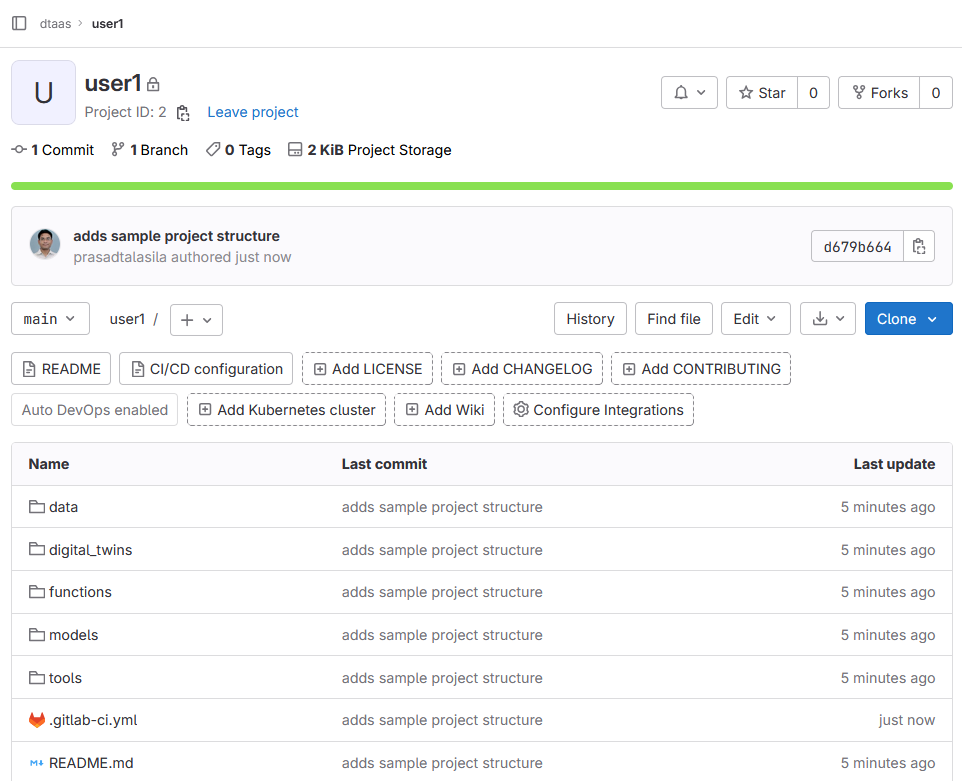
Please pay special attention to .gitlab-ci.yml. It must be a valid
GitLab DevOps configuration. The
example repo provides a sample structure.
For example, with PAT1 as the PAT for the
dtaas/user1 repository, the command to clone the repository is:
After adding the required Library assets:
Next Steps
A GitLab runner should be integrated with the project repository. Runners may already be installed with the DTaaS platform. These can be verified on the runners page. Additionally, custom runners can be installed and integrated with the repository.
The Digital Twins Preview can then be used to access the DevOps features of the DTaaS platform.